Publication Lists
・Original Papers(2025 / 2024 / 2023 / 2022 / 2021 / 2020 / 2019 / 2018 / 2017 / 2016 / 2015 / 2014 / 2013 / 2012 / 2011 / 2010 / 2009 / 2008 / 2007 / 2006 / 2005 / 2004 / 2003 / 2002)
・Review&Books
Review&Books
●Synthesis of Supramolecular Polymers
Takehiro Hirao, Masaya Yoshida, and Takeharu Haino, Handbook of Functional Polymers, Chapter 40: Supramoelcule, Y. Chujo Ed., Springer.
●超分子を用いたフラーレンC70の反応制御-包接することで反応点を制御する-
(解説)久野尚之, 月刊「化学」2024年5月号, p64-65.
●Supramolecular Synthesis of Star Polymers
Supramolecular polymers, in which monomers are assembled via intermolecular interactions, have been extensively studied. The fusion of supramolecular polymers with conventional polymers has attracted the attention of many researchers. In this review article, the recent progress in the construction of supramolecular star polymers, including regular star polymers and miktoarm star polymers, is discussed. The initial sections briefly provide an overview of the conventional classification and synthesis methods for star polymers. Coordination-driven self-assembly was investigated for the supramolecular synthesis of star polymers. Star polymers with multiple polymer chains radiating from metal–organic polyhedra (MOPs) have also been described. Particular focus has been placed on the synthesis of star polymers featuring supramolecular cores formed through hydrogen-bonding-directed self-assembly. After describing the synthesis of star polymers based on host–guest complexes, the construction of miktoarm star polymers based on the molecular recognition of coordination capsules is detailed.
Takeharu Haino and Natsumi Nitta, ChemPlusChem, 2024, 89, e202400014.(Front Cover)
●Cooperativity in molecular recognition of feet-to-feet-connected biscavitands
Octaphosphonate biscavitand and self-folding deep biscavitand show strong positive and negative cooperativity, respectively. The mechanism of the cooperativity is discussed in terms of thermodynamic parameters and the detailed structure of the host-guest complexes. The two cavitand units of both biscavitands are tightly connected via four butylene linkers; thus, they are conformationally coupled, with the first guest binding information transferred to the resting-state cavities. This preorganization modulates the successive guest binding process in strong positive and negative cooperative manners, even though they display structural similarity. The first guest complexation always preorganizes the resting-state cavities where an existing water cluster and a toluene molecule are enthalpically stabilized. Successive guest complexation competes with the water cluster or a toluene molecule, reducing enthalpy gains. However, the desolvation upon successive guest binding processes liberate the solvents within the resting-state cavities. The water cluster is composed of 12 water molecules that are released upon successive guest complexation, resulting in a large entropy benefit. In contrast, toluene desolvation results in a limited entropy benefit. The difference in entropy benefits directs the strong positive or negative cooperativity of the structurally similar biscavitands.
Takeharu Haino, Pure Appl. Chem., 2023, 95, 343-352.
●Nanoarchitectonics of Supramolecular Porphyrins Based on a Bis(porphyrin) Cleft Molecule
This account describes the construction of supramolecular constructs based on our bis(porphyrin) cleft molecule. The bis(porphyrin) cleft molecule was originally synthesized as a tweezer-shaped host molecule for planar guest molecules. A detailed study on the bis(porphyrin) cleft molecule revealed that the bis(porphyrin) cleft molecule forms two kinds of supramolecular structures. One structure is a self-complementary dimer obtained through intermolecular hydrogen bonding, and the other structure is a host-guest complex, in which the electron-rich cleft cavity accommodates electron-deficient guests through donor-acceptor interactions. Through the two supramolecular structures, two distinct supramolecular polymers can be formed through self-complementary dimerization or donor-acceptor host-guest complexation. The supramolecular chain structures were modified by judiciously using two distinct supramolecular structures. In the main text, several results, including the binding capability of our bis(porphyrin) cleft molecule, the formation of supramolecular porphyrin complexes, and the supramolecular polymerization behaviors of the bis(porphyrin) cleft molecule, are reported. In conclusion, the future direction of the bis(porphyrin) cleft molecule is provided.
Takehiro Hirao and Takeharu Haino, J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines, 2023, 27, 966-979
●Development of Supramolecular Polymers with Unique Chain Structures
Takehiro Hirao, Takeharu Haino, Supramolecular Nanotechnology: Advanced Design of Self-Assembled Functional Materials, edited by O. Azzaroni and M. Conda-Sheridan, in Press, VCH-Wiley, Weinheim (ISBN-10: 3527349480)
●Macromolecular architectures constructed by biscalix[5]arene-[60]fullerene host-guest interactions

This focus review is designed to summarize the development of macromolecular architectures formed via biscalix[5]arene–[60]fullerene host–guest interactions. Biscalix[5]arene–fullerene host–guest complexation leads to various macromolecular architectures, including block polymers, star-shaped polymers, cross-linked polymers, and one-handed helical polymers, and host–guest complexation is not prevented by the long polymer chains owing to the high binding affinity between biscalix[5]arene and fullerene. These macromolecular architectures exhibited state-switching natures in response to environmental stimuli. Notably, one of them displayed behavior concordant with those of corresponding covalently linked polymers, including solution viscosity and thermal properties, even though the structures were maintained by relatively weak noncovalent interactions. These demonstrations indicate that biscalix[5]arene–[60]fullerene host–guest interactions can be used to create supramolecularly connected macromolecular architectures that can convert between assembled and disassembled states because of the dynamic nature of noncovalent interactions.
Takehiro Hirao, Polymer Journal, 2022, accepted.
DOI: 10.1038/s41428-022-00732-x
●共沸化合物を簡単に分離する。ー繰り返し使える吸着材料ー
(解説)平尾岳大(Hirao Takehiro), 月刊「化学」2022年8月号, p64-65.
●Integration of Nanographenes and Organic Chemistry – Toward Nanographene-based Two-Dimensional Materials

Graphene and its relatives have received considerable attention from the
fields of physics and chemistry since the isolation of pristine graphene
sheets. Nanographenes (NGs) are graphene fragments that are a few to tens
of nanometers in diameter. Compared to graphene and its relatives, such
as graphene oxides, NGs can be handled more easily, and their large surface
and oxygen functional groups on the edge allow postsynthetic modifications.
The study of NGs is gradually shifting from the development of synthetic
procedures to postsynthetic modification. From the structural point of
view, NGs can be regarded as two-dimensional carbon polymers. Their unique
structures and affinity for organic molecules make NGs excellent scaffolds
for two-dimensional materials, which are now an important topic in organic
and polymer chemistry. In this conceptual article, we introduce the position
of NGs from the perspective of two-dimensional substances and briefly review
both the structural features of NGs and the effects of functionalization
on their physical properties. These are valuable when producing reasonable
strategies for their postsynthetic modifications.
Ryo Sekiya and Takeharu Haino, ChemPhysChem, 2022, 23, e202200311.(Very Important Paper, Front Cover)
●Supramolecular Ensembles Formed via Calix[5]arene-Fullerene Host-Guest Interactions

This minireview introduces the research directions for the synthesis of supramolecular fullerene polymers. First, the discovery of host-guest complexes of pristine fullerenes is briefed. We focus on progress in supramolecular fullerene polymers directed by the use of calix[5]arene-fullerene interactions, which comprise linear, networked, helical arrays of fullerenes in supramolecular ensembles. The unique self-sorting behavior of right-handed and left-handed helical supramolecular fullerene arrays is discussed. Thereafter, an extensive investigation of the calix[5]arene-fullerene interaction for control over the chain structures of covalent polymers is introduced.
Takehiro Hirao and Takeharu Haino, Chem. Asian. J., 2022, e202200344.
●Non-Racemically Twisted Supramolecular Fullerene Polymers
平尾岳大(Hirao Takehiro)・灰野岳晴(Haino Takeharu)
高分子, 71巻, 1号, pp. 6-6, 2022
●Nanographene – A Scaffold of Two-Dimensional Materials

Substances can be divided into 0D to 3D species based on the number of repeating units (atom, ion, and molecule) and their arrangements in space (point, linear, layer, and solid). Discrete substances belong to 0D species, polymers are examples of 1D species, and molecular crystals are 3D species. Most of the substances belong to one of these species. On the other hand, those categorized into 2D species wherein the repeating units organize a layer are less explored. 2D species have a surface and edges. The incorporation of these structural features into a molecular design can realize multifunctionalized systems that are difficult to achieve by conventional organic synthesis. The development of 2D species is, therefore, the frontier of organic, inorganic, and polymer chemistry. Nanographenes (NGs) are suitable scaffolds for realizing 2D species due to several factors, such as chemical stability and oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface and on the edge, allowing postsynthetic modifications. Our group has utilized NGs with tens of nanometers in diameters for developing 2D species. Carboxy groups on the edge enable us to install various substituents into NGs, offering NG-based functional materials. These studies demonstrate that the integration of NGs with organic chemistry can widen the scope of their applications other than optical materials that are a main application of NGs. We introduce our recent studies on the development of NG-based functional materials realized by postsynthetic modifications. We hope that this account will contribute to the development of the chemistry of 2D species.
Ryo Sekiya and Takeharu Haino, Chem. Rec., 2022, 22, e202100257.(Cover Picture)
●Resorcinarene-based Supramolecular Capsules – Supramolecular Functions and Applications

A resorcinarene is a synthetic macrocycle comprising four resorcinol molecules covalently linked by methylene bridges. The interannular bridges produce a cavitand, which possesses a bowl-shaped structure. We have developed supramolecular capsules formed through Ag(I) and Cu(I) coordination-driven self-assembly of cavitands possessing 2,2’-bipyridyl arms at the upper rim. The self-assembled capsules accommodate various molecular guests and supramolecular assemblies possessing acetoxy groups. The host-guest chemistry of the molecular capsules is applied to fabricate supramolecular polymers. This account describes the recent developments in supramolecular chemistry of resorcinarene-based coordination capsules and describes the brief history of resorcinarene-based capsules and related capsules.
Ryo Sekiya, Kentaro Harada, Natsumi Nitta, and Takeharu Haino, Synlett, 2022, 33, 518-530.
●SUPRAMOLECULAR CHEMISTRY OF FULLERENES (Book Chapter)
Takehiro Hirao and Takeharu Haino, Handbook of Fullerene Science and Technology
●ナノグラフェンの有機合成化学による構造修飾と機能発現, Chemical Modification of Nanographenes and Their Functions
Ryo Sekiya and Takeharu Haino, Journal of Synthetic Organic Chemistry, Japan(有機合成化学協会誌), 2021, 79, 743-753.
DOI:10.5059/yukigoseikyokaishi.79.743
●(ナノ)グラフェン
(解説)有機合成化学協会誌2021年8月号, p792
●トップダウン法により得られるナノグラフェンの有機化学
(解説)特集:ナノカーボン材料はどこまで進んだか?
関谷亮(Sekiya Ryo)・灰野岳晴(Haino Takeharu),化学と工業, 2021年6月号,p409-411.
●Programmed Dynamic Covalent Chemistry System of Addition-Condensation Reaction of Phenols and Aldehydes

Application of a dynamic covalent chemistry strategy to the reversible reaction system of resorcinol and α, ω-alkanedials [(CH2)m(CHO)2] (m = 2 ~ 10) in ethanol in the presence of hydrogen chloride (HCl) solution as a catalyst at 80 °C for 48 h afforded the thermodynamically most stable products with high selectivity. The reaction of 1,4-butanedial afforded a ladder polymer containing calixarene skeletons in the main chain in quantitative yield. 1,5-Pentanedial gave Noria, a water-wheel-like cyclic oligomer, in high yield. Calixarene-dimer-type cyclic oligomers were formed selectively from 1,6-hexanedial, 1,8-octanedial, 1,10-decanedial, and 1,12-dodecanedial, while calixarene-trimer-type cyclic oligomers were obtained selectively from 1,7-heptanedial, 1,9-nonanedial, and 1,11-undecanedial. The Noria like macrocyles NoriaPY NoriaMP and NoriaEP could be also synthesized via DCC system using pyrogallol, 3-methoxyphenol, and 3-ethoxyphenol. A triple-ringed[14]arene could be synthesized via DCC system using the reaction of 2-methylresorcinol and m-benzenedicarbaldehyde.
Hiroto Kudo, Daisuke Shimoyama, Ryo Sekiya, and Takeharu Haino, Chem. Lett., 2021, 50, 825-831.
●Supramolecular fluorescent sensors: An historical overview and update

Since as early as 1867, molecular sensors have been recognized as being intelligent “devices” capable of addressing a variety of issues related to our environment and health (e.g., the detection of toxic pollutants or disease-related biomarkers). In this review, we focus on fluorescence-based sensors that incorporate supramolecular chemistry to achieve a desired sensing outcome. The goal is to provide an illustrative overview, rather than a comprehensive listing of all that has been done in the field. We will thus summarize early work devoted to the development of supramolecular fluorescent sensors and provide an update on recent advances in the area (mostly from 2018 onward). A particular emphasis will be placed on design strategies that may be exploited for analyte sensing and corresponding molecular platforms. Supramolecular approaches considered include, inter alia, binding-based sensing (BBS) and indicator displacement assays (IDAs). Because it has traditionally received less treatment, many of the illustrative examples chosen will involve anion sensing. Finally, this review will also include our perspectives on the future directions of the field.
Chenxing Guo, Adam C. Sedgwick, Takehiro Hirao, and Jonathan L. Sessler, Coord. Chem. Rev., 2021, 427, 213560.
●Edge Functionalized Nanographenes

Nanographenes (NGs) have recently emerged as new carbon materials. Their nanoscale size results in a size-dependent quantum confinement effect, opening the band gap by a few eV. This energy gap allows NGs to be applied as optical materials. This property has attracted researchers across multiple scientific fields. The photophysical properties of NGs can be manipulated by introducing organic groups onto their basal planes and/or into their edges. In addition, the integration of organic functional groups into NGs results in NG-based hybrid materials. These features make the postsynthetic modification of NGs an active research area. Since obtainable information on chemically functionalized NGs is limited due to their nonstoichiometry and structural uncertainty, their structural characterization requires a combination of multiple spectroscopic methods. Therefore, information on the characterization procedures of recently published chemically functionalized NGs is of value for advancing the field of NG-based hybrid materials. The present review focuses on the structural characterization of chemically functionalized NGs. We hope this review will help to advance this field.
Ryo Sekiya and Takeharu Haino, Chem. Eur. J., 2021, 27, 187-199. (This article was selected as a Review Showcase.)
●Feet‐to‐Feet‐Connected Multitopic Resorcinarene Macrocycles

The past three decades have witnessed extraordinary advances in the preparation of macrocycles from a resorcinarene platform. Bridging two or more resorcinarene units through multipoint connections produces multitopic resorcinarene‐based hosts. The unique properties arising from multivalency offer diverse applications, such as molecular flasks, molecular machines, and supramolecular polymers. The face‐to‐face connection of two or more resorcinarenes results in a convergent, expanded guest binding space in which many large guests can be accommodated. In contrast, the feet‐to‐feet connection provides an extroverted, ditopic feature that can lead to different applications. Herein, we highlight the synthesis of extroverted, multitopic resorcinarene macrocycles and discuss their fascinating functions, such as molecular recognition, allosteric guest binding, and supramolecular polymerization.
Daisuke Shimoyama and Takeharu Haino, Asian. J. Org. Chem., 2020, 1718-1725.
●灰野岳晴教授のプロフィールがAngew. Chem. Int. Ed.に掲載されました。
●Chemically Funtionalized Two-Dimensional Carbon Materials
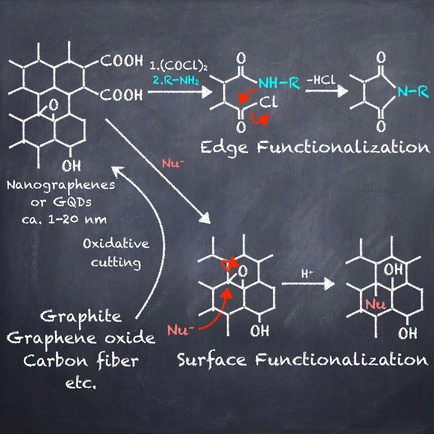
Nanographenes (NGs), also known as graphene quantum dots, have recently been developed as nanoscale graphene fragments. These nanocarbon species can be excited with UV light and emit light from the UV‐to‐visible region. This photoemission has received great attraction across multiple scientific fields. NGs can be produced by cutting off carbon sources or fusing small organic molecules to grow graphitic structures. Furthermore, the organic synthesis of NGs has been intensely studied. Recently, the number of research papers on postsynthetic modifications of NGs has gradually increased. Installed organic groups can tune the properties of NGs and provide new functionalities, opening the door for the development of sophisticated carbon‐based functional materials. This review sheds light on recent progress in the postsynthetic modification of NGs and provides a brief summary of their production methods.
Ryo Sekiya, and Takeharu Haino, Chem. Asian J.,2020, 15, 2316-2328
●Supramolecular Polymerization and Functions of Isoxazole Ring Monomers

Head-to-tail dipole-dipole arrays of isoxazole rings lead to supramolecular helical assemblies where the assembly and disassembly are regulable based on temperature and solvent properties. The cooperative supramolecular polymerization characterized by a two-step polymerization consisting of nucleation and elongation is driven by the multiple dipole array as well as the induced dipoles in the supramolecular organization. The helical supramolecular assemblies are fabricated with the aid of multiple dipole–dipole interactions. The chiroptical properties, such as CD and CPL, are determined by the right-handed and left-handed helicities of the supramolecular organizations, which are directed by the stereogenic side chains. The AIE and AIEE are established in the supramolecular assemblies. The AIE feature of the platinum complex is inherent in the supramolecular assemblies, which results in luminogenic micelles. Emissive supramolecular micelles are fabricated. In this review, these aspects are briefly described, emphasizing the importance of the intermolecular dipole-dipole interactions in supramolecular chemistry.
Takeharu Haino and Takehiro Hirao, Chem. Lett., 2020, 49, 574-584.
●トップダウン法により得られる化学修飾ナノグラフェン
Nanographenes, which are nanoscale graphene fragments, can be obtained by cutting off carbonaceous materials. This procedure, so-called top-down method, allows the gram-scale production of nanographenes. Our group has utilized these nanographenes for developing carbon-based functional materials. The installation of organic groups into the edge of nanographenes realized functionalized nanographenes. These nanographenes exhibit interesting properties, such as white-light emission, supramolecular polymerization and near-infrared emission.
Ryo Sekiya and Takeharu Haino, ファインケミカル, 2020年, 1月
●Designer Supramolecular Polymers with Specific Molecular Recognitions

Supramolecular polymers are members of an emergent class of polymer materials that exhibit designability and flexibility. This article describes how supramolecular polymers can be synthesized by taking advantage of our host–guest structures based on a calix[5]arene, a bisporphyrin, and a self-assembled capsule. Linear and two-dimensional fullerene nanostructures can be fabricated using the designed monomer structures. The porphyrin donor–acceptor interaction directs the supramolecular polymerization, resulting in linear porphyrin polymers that behave similarly to a conventional polymer chain in solution, even though their structures are dynamic and time-averaged. The fragile supramolecular polymer chains are cross-linked to fabricate a robust self-standing film. The sequence reorganization of the supramolecular homopolymer is established by competitive ditopic guest complexation. The sequence-controlled terpolymer is fabricated via self-sorting behavior. The postmodifications of the supramolecular polymer chains, as well as the polymer chains themselves, are achieved by grafting and non-covalent cross-linking to regulate the macroscopic properties and structures of the polymer main chains. These uniquely organized polymers are fabricated on a nanoscale.
Haino, Takeharu, Polym. J., 2019, 51, 303-318
●Supramolecular Polymerization Engineered with Molecular Recognition
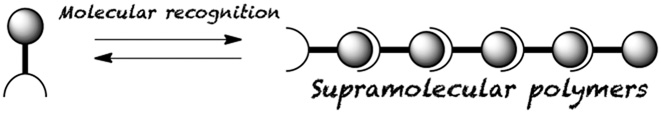
Supramolecular polymeric assemblies represent an emerging, promising class of molecular assemblies with enormous versatility compared with their covalent polymeric counterparts. Although a large number of host–guest motifs have been produced over the history of supramolecular chemistry, only a limited number of recognition motifs have been utilized as supramolecular connections in polymeric assemblies. This account describes the molecular recognition of host molecules based on calix[5]arene and bisporphyrin that demonstrate unique guest encapsulations; subsequently, these host–guest motifs are applied to the synthesis of supramolecular polymers that display polymer‐like properties in solution and solid states. In addition, new bisresorcinarenes are developed to form supramolecular polymers that are connected via a rim‐to‐rim hydrogen‐bonded dimeric structure, which is composed of two resorcinarene moieties.
Haino, Takeharu, Chem. Rec., 2015, 15, 837-853
●Supramolecular Chemistry: From Host-guest Complexes to Supramolecular Polymers
Combining the concepts of supramolecular chemistry with material science has led to the development of supramolecular polymer chemistry. Although a large number of host-guest motifs have been produced, only a limited number of recognition motifs have been utilized as supramolecular connections within polymeric assemblies. In this account, we describe the molecular recognition of host molecules based on a calix[5]arene and a bisporphyrin, demonstrating unique guest encapsulations; subsequently, these host-guest motifs were applied to the synthesis of supramolecular polymers that display polymer-like properties in both solution and solid states. In addition, we disclose that bisresorcinarenes form supramolecular polymers that are connected via a hydrogen-bonded rim-to-rim dimeric structure, which is composed of two resorcinarene moieties.
Haino, Takeharu, J. Synth. Org. Chem. Jpn., 2013, 71, 1172-1181
DOI:10.5059/yukigoseikyokaishi.71.1172
●超分子化学を用いる分子配列構造の制御
灰野岳晴, Organometallic News, 2013, 2, 54-60
●Molecular-recognition-directed formation of supramolecular polymers
Haino, Takeharu, Polym. J., 2013, 45, 363-383
