Publication Lists
・Original Papers(2025 / 2024 / 2023 / 2022 / 2021 / 2020 / 2019 / 2018 / 2017 / 2016 / 2015 / 2014 / 2013 / 2012 / 2011 / 2010 / 2009 / 2008 / 2007 / 2006 / 2005 / 2004 / 2003 / 2002)
・Review&Books
2016


●Allostery in Guest Binding of Rim-to-Rim-Connected Homoditopic Biscavitands

Rim‐to‐rim‐connected phosphonate biscavitands 1a and 1b were synthesized. Crystal structure analysis and variable‐temperature NMR spectroscopy studies reveal that 1a is more rigid in conformation than 1b. Biscavitands 1a and 1b bind cationic guests G1–G3 through hydrogen bonding and CH–π interactions, demonstrating positive and negative allosteric effects, respectively. The allosteric effects in guest binding are associated with the conformational flexibilities of 1a and 1b. The positive allosteric effect of 1a is directed by the tightly connected cavities, in which information of the first guest binding is transferred to the remaining cavity, which becomes preorganized. In contrast, a slightly negative allosteric effect is found in more‐flexible 1b.
Shimoyama, Daisuke; Yamada, Hitomi; Ikeda, Toshiaki; Sekiya, Ryo; Haino, Takeharu, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2016, 3300-3303(Front Cover)
●Synthesis and Properties of Novel Optically Active Platinum-containing Poly(phenyleneethynylene)s

The dehydrochlorination coupling polymerization of N-(3,5-diethynylbenzoyl)-l-alanine dodecylamide 1 with platinum (Pt) chlorides having pyridine, bipyridine, and phenanthroline ligands 2a–2d gave novel optically active poly(phenyleneethynylene)s [poly(1-2a)–poly(1-2d)] bearing Pt in the main chains. The Z-average diameters of the polymers ranged from 453 to 1081 nm. Poly(1-2a) exhibited CD signals assignable to aggregates, and formed regulated twisted structures with height of 540 ± 70 nm and pitch of 62 ± 6 nm, which were confirmed by AFM measurements.
Otaki, Yoshinori; Marumoto, Manabu; Miyagi, Yu; Hieran, Takehiro; Haino, Takeharu; Sanda, Fumio, Chem. Lett.2016,45, 937-939
●Cooperative Self-Assembly of Carbazole Derivatives Driven by Multiple Dipole-Dipole Interactions
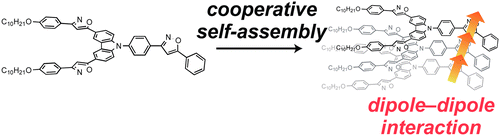
Carbazole possessing phenylisoxazoles self-assembled in a cooperative manner in decalin. X-ray crystal structure analysis revealed that the isoxazole dipoles align in a head-to-tail fashion. DFT calculations suggested that the linear array of dipoles induced the polarization of each dipole, leading to an increase in dipole–dipole interactions. This dipole polarization resulted in cooperative assembly.
Ikeda, Toshiaki; Iijima, Tatsuya; Sekiya, Ryo; Takahashi, Osamu; Haino, Takeharu, J. Org. Chem., 2016, 81, 6832-6837
●Synthesis of a Pentacene-Type Silaborin via Double Dehydrogenative Cyclization of 1,4-Diboryl-2,5-disilylbenzene
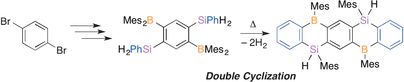
A new pentacene‐type silaborin, in which three benzene rings are bridged by silicon and boron atoms, has been synthesized and characterized by using NMR spectroscopy and X‐ray crystallographic analysis. The precursor, 1,4‐bis(dimesitylboryl)‐2,5‐bis(phenylsilyl)benzene (4), was prepared by stepwise introduction of a silyl group and a boryl group to a benzene ring starting from 1,4‐dibromobenzene. Double cyclization of 4 proceeds by a H‐Mes exchange and a B‐H/C‐H dehydrogenative condensation to afford pentacene‐type silaborin 5. X‐ray crystal structure analysis reveals that 5 adopts a bent structure rather than a planar one. UV/Vis spectra and DFT calculations for 5 reveal a lowering of the LUMO energy level compared with corresponding anthracene‐type 3.
Hirofuji, Tatsuya; Ikeda, Toshiaki; Haino, Takeharu; Yamamoto, Yohsuke; Kawachi, Atsushi, Chem. Eur. J., 2016, 22, 9734-9738.
●Chemical Functionalisation and Photoluminescence of Graphene Quantum Dots
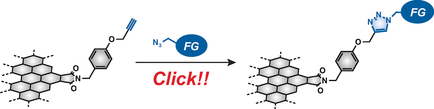
Chemical modification of graphene quantum dots (GQDs) can influence their physical and chemical properties; hence, the investigation of the effect of organic functional groups on GQDs is of importance for developing GQD–organic hybrid materials. Three peripherally functionalised GQDs having a third‐generation dendritic wedge (GQD‐2), long alkyl chains (GQD‐3) and a polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane group (GQD‐4) were prepared by the CuI‐catalysed Huisgen cycloaddition reaction of GQD‐1 with organic azides. Cyclic voltammetry indicated that reduction occurred on the surfaces of GQD‐1–4 and on the five‐membered imide rings at the periphery, and this suggested that the functional groups distort the periphery by steric interactions between neighbouring functional groups. The HOMO–LUMO bandgaps of GQD‐1–4 were estimated to be approximately 2 eV, and their low‐lying LUMO levels (<−3.9 eV) were lower than that of phenyl‐C61‐butyric acid methyl ester, an n‐type organic semiconductor. The solubility of GQD‐1–4 in organic solvents depends on the functional groups present. The functional groups likely cover the surfaces and periphery of the GQDs, and thus increase their affinity for solvent and avoid precipitation. Similar to GQD‐2, both GQD‐3 and GQD‐4 emitted white light upon excitation at 360 nm. Size‐exclusion chromatography demonstrated that white‐light emission originates from the coexistence of differently sized GQDs that have different photoluminescence emission wavelengths.
Sekiya, Ryo; Uemura, Yuichiro; Naito, Hiroyoshi; Naka, Kensuke; Haino, Takeharu, Chem. Eur. J., 2016, 22, 8198-8206.
●Hydrogen-bonded hexameric cluster of benzyl alchol in the solid state polymeric organization of p-tert-Butylcalix[5]arene
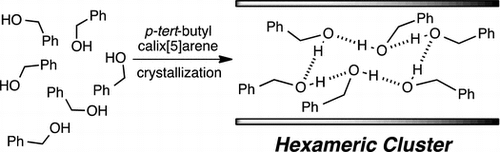
An uncommon hydrogen-bonded hexameric cluster of benzyl alcohol (2) was formed in hydrophobic space in the layered organisation of the one-dimensional polymeric zigzag array of 1 in the solid state. The hexameric cluster adopted a distorted cyclohexane-like (12) O–H⋯O hydrogen bond network. The formation of the hexameric cluster was quite sensitive to a tiny structural difference of guests; phenylethylalcohol (3), phenol (4), benzyl amine (5) and aniline (6) did not form any hexameric cluster. The packing coefficient of 0.53 suggested that the hexameric cluster nicely filled the hydrophobic space, which most likely resulted in the effective van der Waals contacts that stabilised the supramolecular organisation composed of the hexameric cluster and the polymeric array of 1 in the solid state.
Kajiki, Yasunori; Sekiya, Ryo; Haino, Takeharu, Supramol. Chem.2016,28, 444-449
DOI:10.1080/10610278.2015.1117084
●Photoresponsive Toroidal Nanostructure Formed by Self-assembly of Azobenzene-Functionalized Tris(phenylisoxazolyl)benzene
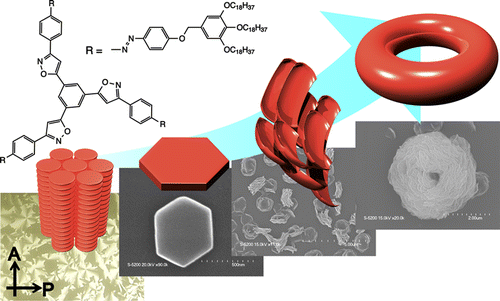
The self-assembly of tris(phenylisoxazolyl)benzene 1b with photochemically addressable azobenzene moieties produced toroidal nanostructures, the formation and dissociation of which were reversibly regulated upon photoirradiation. 1b displayed a mesogenic behavior. In the solution, the stacked assemblies along with their C3 axes were formed. In the mesophase, two molecules of 1b most likely adopted the antiparallel arrangement to stabilize the columnar organization. This assembling behavior most likely triggered the development of the supramolecular toroidal nanostructures.
Adachi, Hiroaki; Hirai, Yuko; Ikeda, Toshiaki; Maeda, Makoto; Hori, Ryo; Kutsumizu, Shoichi; Haino, Takeharu, Org. Lett., 2016, 18, 924-927.
DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.5b03622
●Frozen Dissymmetric Cavities in Resorcinarene-Based Coordination Capsules
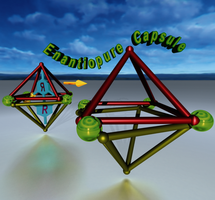
By introducing slight structural modifications to a D4‐symmetric coordination capsule, we succeeded in isolating the nearly enantiopure capsules (P)‐ and (M)‐2 a(BF4)4. Chiral guest, dibenzyl 4,4′‐diacetoxy‐6,6′‐dimethyl‐[1,1′‐biphenyl]‐2,2′‐dicarboxylate (3) was encapsulated within the dissymmetric cavity of 2 a(BF4)4, resulting in a high diastereoselectivity of >99 % de. The encapsulated guest was successfully removed from the complex without racemization through precipitation of the empty capsule. CD spectra confirmed that the chirality of the capsule was maintained in THF and 1,4‐dioxane for long periods, whereas a small amount of acetonitrile accelerated racemization of the empty capsule. The activation parameters of the racemization reaction were determined in dichloromethane and 1,2‐dichloroethane, resulting in positive enthalpic contributions and large negative entropic contributions, respectively. Accordingly, the racemization fits a first‐order kinetic model. Mechanically coupled Cu+‐2,2′‐bipyridine coordination centers were responsible for the high‐energy barrier of racemization and led to the unique chiral memory of the dissymmetric cavity, which was turned off by the addition of acetonitrile.
Imamura, Taisuke; Maehara, Takeshi; Sekiya, Ryo; Haino, Takeharu, Chem. Eur. J., 2016, 22, 3250-3254
●Induced-Fit Molecular Recognition of Alkyl Chains in p-tert-Butylcalix[5]arene in the Solid state
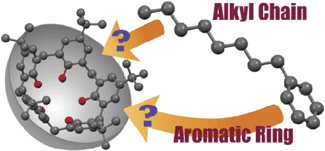
p-tert-Butylcalix[5]arene 1 recognized conformationally flexible aliphatic hydrocarbons (hexane 2, heptane 3, octane 4, nonane 5, decane 6, undecane 7, and dodecane 8) and monoalkyl benzenes (toluene 10, ethylbenzene 11, propylbenzene 12, butylbenzene 13, hexylbenzene 14, and octylbenzne 15) to form host–guest complexes. X-ray diffraction study has revealed that the alkyl chains of 11–15 were selectively recognized by 1, whereas host 1 recognized the aromatic ring of 10. The alkyl chain termini of 3, 4, 6–8, 11–13, and 15 adopted unusual folded conformations in the cavity. M06-2X/6-31G(d,p) level of calculations revealed that the mutual induced-fit shape adjustments between the calix[5]arene cavity and the flexible guests play a key role in maximizing the host–guest interactions directed by the C(sp3)–H/π interactions, leading to the unusual conformations of the alkyl chain termini of the guests and the selective binding of the alkyl chains in the solid state.
Kajiki, Yasunori; Sekiya, Ryo; Yamasaki, Yutaro; Uemura, Yuichiro; Haino, Takeharu, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn.2016,89, 220-225 (SelectedPaper)
●Synthesis of Linear [5]Catenanes via Olefin Metathesis Dimerization of Pseudorotaxanes Composed of a [2]Catenane and a Secondary Ammonium Salt
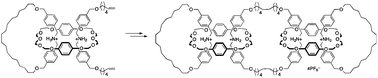
[5]Catenanes were synthesized by olefin metathesis dimerization. The reaction of pseudorotaxanes, which were derived from a [2]catenane and one equivalent of an ammonium salt bearing two terminal olefins in dichloromethane, with a catalytic amount of Grubbs catalyst afforded linear [5]catenanes in 12% yield. Intermolecular and intramolecular olefin metathesis reactions were controlled by the length of the alkyl chain of the ammonium salts.
Iwamoto, Hajime; Tafuku, Shinji; Sato, Yoshihiko; Takizawa, Wataru; Katagiri, Wataru; Tayama, Eiji; Hasegawa, Eietsu; Fukazawa, Yoshimasa; Haino, Takeharu, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 319-322
●Solvent-induced Emission of Organogels Based on Tris(phenylisoxazolyl)benzene
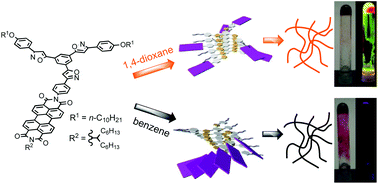
Luminescent organogels based on tris(phenylisoxazolyl)benzene possessing perylenebisimide 1 were synthesized. The emission properties of the gels varied depending on the solvent properties: 1,4-dioxane gel was highly emissive, pyridine gel was moderately emissive, and benzene gel was non-emissive.
Ikeda, Toshiaki; Masuda, Tetsuya; Takayama, Midori; Adachi, Hiroaki; Haino, Takeharu, Org. Biomol. Chem.2016,14, 36-39(Front Cover)